
13 May Comprehensive Guide to Penetration Testing (Security Testing)
Recent trends show that many organisations and companies are digitising their business, operations, and process due to many favorable factors like scalability, efficiency, and flexibility.
Along with its many advantages, digitising also comes with many disadvantages. Primarily, this involves organisations and companies underestimating the new technologies that they are exposed to. Data breaches and cyber-attacks are becoming a new norm.
The possibility that the attacker can take full control of your IT infrastructure becomes extremely likely if the company doesn’t undertake regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing.
The company needs to have a proper procedure or a system to detect, respond and recover from the attacks. Here the focus will be on why there is a need for penetration testing, the penetration testing methods, and the procedures to follow to perform a successful pen test.
What is Penetration Testing?
Penetration testing encompasses various manual and automated techniques to simulate an attack on an organisation’s information systems. An ethical hacker or pen tester generally conducts pen testing, who tries to break into the corporate information systems and identify and exploit known and unknown vulnerabilities before an actual attacker or a malicious actor does.
The security tester primarily carries out an active analysis of the target system to identify any potential threats or vulnerabilities that could result from improper system configuration, system infrastructure flaws or operational incompetency.
Why should an Organisation Carry out Pen Testing?
- To determine threats and weaknesses in the overall infrastructure, both hardware, and software, to develop a sound security control system.
- To uncover gaps within the organisation existing security posture and address them specifically and effectively.
- To ensure that the security system or controls in place are effective and mitigate the risks of an attack.
- To prioritise attack vectors and secure attack avenues that are more prone to an attack.
- To discover existing bugs in the security control system and fix them.
- To determine and detect the possible magnitude of the breach and to improve the overall security response time to an attack.
Read Also: Importance of Security Assessments
Penetration Testing Stages
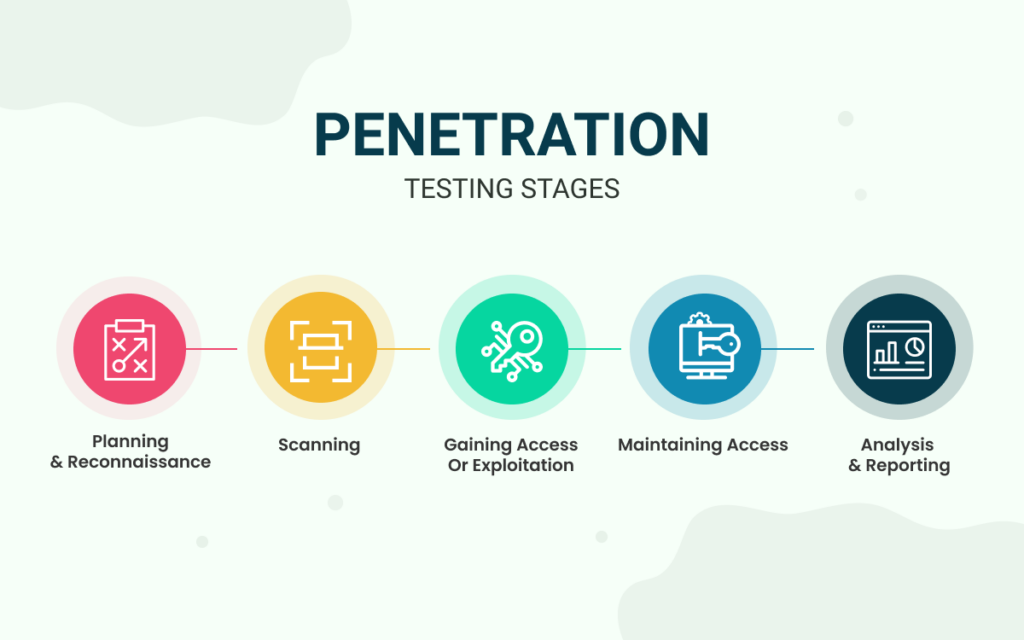
Security test or Penetration test involves simulated breaching of any number of applications or systems such as application protocol interfaces, front-end or back-end servers, security infrastructure, and unsensitised inputs to detect vulnerabilities and threats.
The pen testing process usually includes five stages and helps the organisation to fine-tune their environment for fixing security loopholes.
The stages are as follows:
1. Planning and Reconnaissance
This stage includes defining the scope, priorities, and goals to be achieved. It also states the primary critical systems to be tested or addressed and types of test to be performed.
The reconnaissance stage includes gathering intelligence like passive and active information on network and domain names or mail servers et al. of the target system to better understand how a target works and its potential entry points.
2. Scanning
This stage involves understanding how the target system responds to various automated intrusion attempts and attacks. This is typically done using following.
- Static Analysis – Inspects the application source code before a program is run by comparing it to a set of coding rules followed by debugging
- Dynamic Analysis – is the testing and evaluation of the security system by executing data in real-time. The objective here is to find errors or vulnerabilities in real-time by scanning the application or systems using automated security scanning tools. Static or dynamic analysis is followed by manual verification of vulnerabilities or errors to eliminate false positives.
3. Gaining Access or Exploitation
In this stage, the vulnerabilities identified are actively exploited to gain access to the system or valuable information. The vulnerabilities can be exploited by escalating privileges, stealing data, intercepting traffic and injecting malicious code to understand or observe the magnitude of the damage caused.
4. Maintaining Access
The objective of this stage is to check if persistence access can be maintained after gaining access to the application or its underlying system. The longer the attacker maintains access to the system, the more in-depth access he/she gains. The goal is to imitate and detect advanced persistent threats that often remain in a system without being detected.
5. Analysis and Reporting
The results of the test are then compiled into a detailed report. The report primarily contains vulnerabilities that were exploited, sensitive data that was breached and accessed, and the amount of time the security tester could remain in the system before getting detected.
Penetration Testing Methods
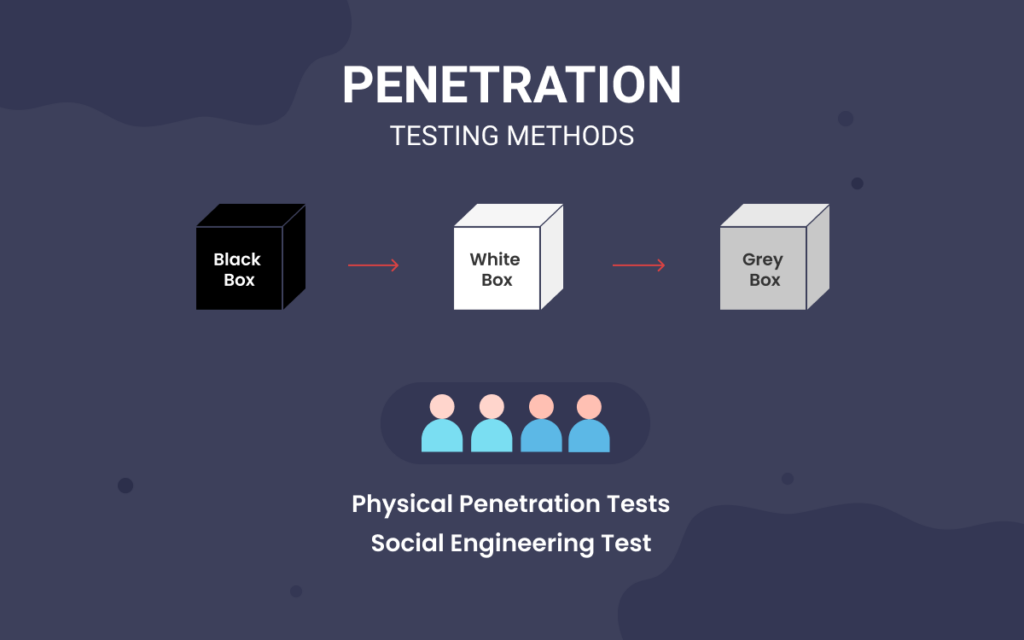
Many penetration testing methods are depending upon the security system and the level of motivation of the organisation. A security expert or a Cyber Security Firm should help you choose or determine a perfect match as per the organisation’s requirements.
The different types of pen testing methods are as follows. Depending upon the type of information a security expert or a pen tester has, the methods can be divided into:
Black Box
A black box assessment is carried out with little information provided to the pen tester. The security consultant or the tester will have very limited knowledge about the security control system or the infrastructure. Typically, the consultant will undertake the reconnaissance methodology to gain information about the system and security infrastructure.
White Box
In the white box assessment, the tester or the consultant is provided with information and detailed documentation regarding the infrastructure, applications, equipment’s and security control system such as system architecture documents, source code and more. It is a comprehensive assessment method to identify and detect external as well internal vulnerabilities.
Grey Box
In this assessment method, the tester is provided with user-level knowledge and information needed to assess the security control system. The testers are also granted limited access and partial knowledge to the web applications and the internal network infrastructure.
Physical Penetration Tests
The organisation should be wary of hackers adopting a physical approach to gain facility access either as a standalone attack or to complement their technical attacks. The following are physical penetration tests:
- Scoping Unsecured Areas: In this method, hackers’ scope or search areas or systems that are vulnerable and are more prone to a breach or an attack. This may include smoking areas, maintenance docks, and unguarded entrances with the least resistance and visibility to gain facility access.
- Piggybacking: Piggybacking, tailgating or eavesdropping are some methods wherein a hacker closely follows the employees or maintenance workers that have access to the facility area.
Social Engineering Test
These tests verify the Human Network of an organisation. This test helps determine and secure an attack from within an organisation from the employee who is either initiating an attack or has his credentials or privileged access compromised. The types of attacks are:
- Phishing: A deceptive method wherein personal information is gained by sending across malicious or infected codes via mail or messages.
- Pretexting: Pretexting is a form of identity theft wherein the hackers present themselves as someone else who is a part of an organisation and gain access to the security infrastructure or sensitive data.
Read Also: The Why and How of Social Engineering
Most Common Types of Pen Testing / Security Testing:

Network Penetration Testing
A network penetration test is the most common and in-demand pen test method, which helps detect and exploit vulnerabilities in the network system or infrastructure. There are three types of Network pen testing, external, internal, and wireless.
External Network Penetration Testing: The external network pen test helps you probe how robust your external network system responds to threats. The common tests included in the External network pen test are Internet-based pen testing which identifies vulnerabilities and weaknesses within the system that are exposed to the internet.
This test generally targets network areas like Firewall configuration, firewall bypass, IPS deception and DNS level attacks. Vulnerability scanning is a type of test or an automated process that utilises the shelf tools to scan and detect known vulnerabilities in your system.
A combination of automated and manual exploitation techniques is a process wherein the vulnerabilities after detection are targeted, and a variety of attacks are simulated against these weaknesses with an aim to completely take over the internet-facing systems.
Internal Network Pen Testing: This test includes identifying or detecting security network weaknesses within your internal systems or infrastructure. This test too includes vulnerability scanning and exploitation techniques to detect the vulnerabilities and then exploit them to see how the internal systems respond.
The internal network pen test fundamentally evaluates the potential of an exploit by an internal user or an unauthorised attack by an employee of the organisation, such as potential unauthorised access and leak of personal credentials or information.
Wireless Penetration Testing: Wireless systems allow hackers or attackers an opportunity to hack into or infiltrate the organisation’s network security system.
Wireless pen testing allows access to the consultant into the system who then tries to detect vulnerabilities and exploit them allowing them privileged access to sensitive information.
Thus, wireless pen testing allows the consultants to demonstrate the potential impact of the breach in the wireless network.
Web Application Penetration Testing
The web application is an integral part and function of the organisation. A compromised web application may cause data breaches and leak sensitive information.
Web application penetration testing is a testing method wherein applications on the network are checked for any vulnerabilities or security issues caused by faulty or insecure development, weak design, or improper coding.
Read Also: All About Web Application Penetration Testing
Mobile Application Penetration Testing
Similar to web applications, mobile applications too, is an important arena for an organisation. Mobile application penetration testing or security testing is an empowered and simulated hacking attempt against a native mobile application running on devices such as Android, Windows, and iOS.
Mobile application pen testing allows the organisation to discover and exploit vulnerabilities in their mobile applications and the way it communicates and transmits data with the backend systems.
Read Also: Mobile Phone Security Tips
Penetration Testing Tools:

There is a full suite of automated testing tools available now, which allows you to carry out penetration testing efficiently. The following are some of the well-known tools used for Pen testing:
Kali Linux
Kali Linux is a Linux-based operating system containing vast arrays of tools and can be used for end-to-end penetration testing from information gathering to reporting.
It is a widely used penetration testing platform that optimises the offence and not defence. It is an open-source project and provides tool listings, version cracking and meta-packages.
Kali has over 600 ethical hacking tools and contains special tools used for brute force password cracking. Tools include vulnerability analysis, web applications, information gathering, wireless attacks, reverse engineering, password cracking, spoofing, sniffing and other advanced exploitation tools.
Metasploit
Metasploit is the most used automated exploitation framework. Metasploit helps in targeting a system, detect the vulnerabilities and help to exploit the vulnerabilities.
It help in managing security assessments, detects threats and flaws, and probable weak points. This tool helps set up a watertight and robust security control system that is difficult to breach. The GUI of Metasploit is easy to use and is open-source software.
Metamodule part of Metasploit pro version can be used for network segmentation testing meaning it will identify where it was able to reach the segmented network or not.
Wireshark
Wireshark is a network analyser tool that captures and interprets network traffic. It provides both offline analysis and network real-time capture options.
Generally used to understand data packets flow and TCP/IP issues. It provides details of packet moments and network activities.
ZED attack Proxy
This tool is similar to one of the most popular proxy and scanning tool BURP suite and is almost as effective except that it is completely free.
ZAP positions itself between your browser and the website you are testing and creates a proxy that allows the tester to intercept the traffic and modify or alter it. It is ideal for developers and testers who are new to penetration testing or security testing.
Aircrack
Aircrack NG is a set of tools and a software suite that helps you attack and defend wireless networks. The tools package includes a detector, packet sniffer, WEP/WPA cracker, and so on.
Aircrack primarily intercepts the packets, captures them, and then reads the packet patterns to crack the wireless system. Aircrack is open-source software and mainly used to check Wi-Fi connections
John the Ripper
Passwords are the most vulnerable and are easy to attack in an information system. JTR is a password-cracking tool that cracks encryption and provides the password.
It includes a customisable cracker and identifies different password hashes. It can run efficiently with sturdy hardware and crack passwords in no time.
Read Also: Popular Penetration Testing Tools
Costing and Budgeting of Penetration Testing

The costing and budgeting depend on several factors and is not constant. The following factors affect the cost of penetration testing service.
Objective: The pricing fairly depends on the objectives or aims you wish to accomplish. Whether it is to test the physical access of a small organisation or transmission station of a utility, the pricing differs. The size is a factor when it comes to pricing.
For instance, the pricing differs when an entire network, including external and internal networks, is to be tested compared to just applications. The information you make available to the security tester also affects the pricing. The greater and more complex the objectives in number, the higher is the pricing.
Scope: Scope helps to determine organisations objectives and amount of time a tester or a consultant will require to complete the project. The duration and the cost are directly proportional to each other.
For instance, a web application facing a large customer portal and users might take more time than applications with a low user functionality. The lesser the degree of complexity and scope, the lesser is the price.
Methodology or Approach: The approach an organisation adopts also affects the pricing. Some organisations may undertake automated vulnerability scanning, which is the basic testing level and addresses the basic issues.
At the same time, some companies may opt for a comprehensive approach to pen testing, which includes detecting the threats and vulnerabilities and their exploitation to demonstrate their complete impact. The comprehensive approach costs higher.
Skills: Like any other industry, skills play a vital role in the Cyber Security Industry. You obviously pay more to skilled consultants and expert security testers who have in-depth knowledge and experience of the systems in your industry than testers who have limited resources or simply basic knowledge.
Re-testing: Re-testing is a process that many organisations often overlook. Once the vulnerabilities have been detected and worked upon to build a more robust system that can mitigate attacks, Re-testing is essential to check whether the Pen test has the desired effect or not.
The pricing policy differs when Retesting is taken into consideration.
Read Also: How to Plan and Manage Cyber Security Budget?
Conclusion
In the current global economy, when we hear of cyber-attack instances almost every day, penetration testing has become an indispensable activity for any business that has any form of digital presence.
It is also imperative that pen testing be performed periodically and not be considered as a “one-off” activity. With the growth and scalability of could technology, several start-ups set up operations on a SaaS model. Being new entrants and relatively young in the business lifecycle, they tend to de-prioritise application security.
However, this could prove to be costly as they are lucrative targets for hackers, and one minor incident could result in the business ending even before it started.
Cyber threats and vulnerabilities in systems change and evolve constantly; Cyber Security Experts and Service Providers like SecureTriad keep up with the trends and are equipped with the necessary skills, expertise, and tools to help keep an organisation’s systems safe.
To know more about pen testing and discuss methods for securing your business assets, contact SecureTriad: a leading penetration testing company.



